Above-ground Biomass Carbon
Annual estimates of carbon stored in vegetation above the soil surface, monitoring ecosystem carbon dynamics since 2001.
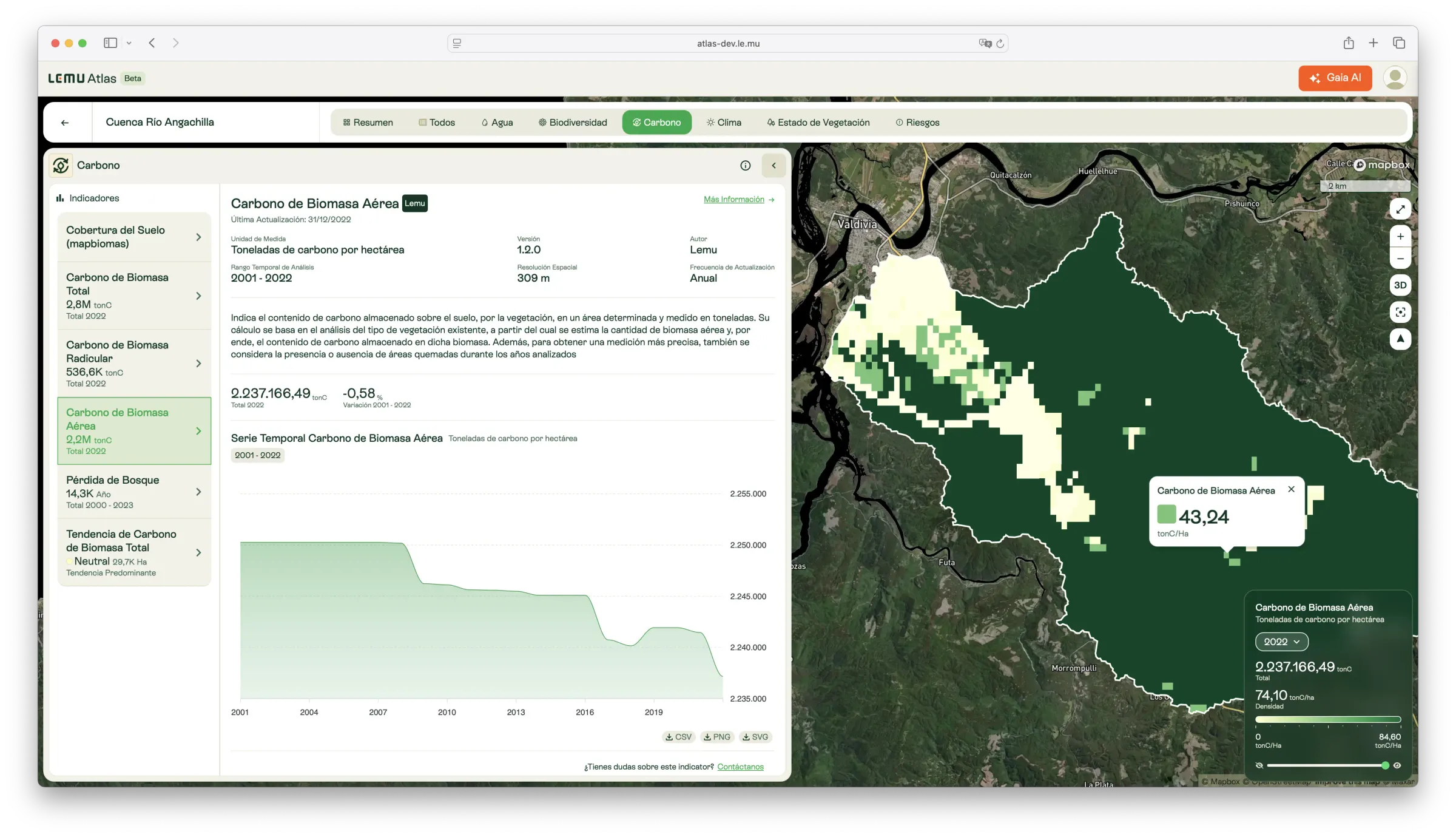
Description
This indicator measures the amount of carbon stored in above-ground biomass — the portion of vegetation that grows above the soil. Estimates are expressed in tonnes of carbon per hectare and are available annually from 2001 onwards.
Calculations are based on vegetation type and land cover, integrating burned-area data to refine accuracy. Monitoring above-ground biomass carbon provides insights into how ecosystems evolve, allowing detection of reductions from deforestation or fires and increases from reforestation or natural regrowth.
What it measures
- Carbon stored in vegetation above the soil.
- Annual changes in above-ground biomass carbon (2001–2022).
- Contribution of above-ground biomass to total ecosystem carbon stocks.
How to interpret
- Lower values: indicate disturbed or degraded ecosystems with reduced vegetation.
- Higher values: signal intact or dense vegetation with high carbon storage.
- Changes over time reveal disturbance (losses) or recovery (gains).
Unit / Scale
Tonnes of carbon per hectare (tC/ha).
Temporal coverage: 2001–2022.
Spatial resolution: 309 m.
Update frequency: Annual.
Author / Source
Lemu — integrating global land cover, biomass, and fire datasets.
Key sources include:
- Copernicus Climate Change Service (C3S): Land cover classification maps.
- Gibbs, H. K., & Ruesch, A. — IPCC Tier-1 Global Biomass Carbon Map (2000).
- Giglio, L., Justice, C., Boschetti, L., & Roy, D. (2021). MODIS Burned Area Dataset (NASA EOSDIS).
🔗 https://climate.copernicus.eu
🔗 https://daac.ornl.gov/cgi-bin/dsviewer.pl?ds_id=932
Applications in Atlas
- Provide annual monitoring of carbon storage in vegetation.
- Detect forest loss, degradation, or fire events.
- Track the effectiveness of restoration and conservation efforts.
- Support climate reporting, carbon offset projects, and sustainable land-use planning.